Public Announcement: You Can Now Debug Programs Using GDB on Redox OS
By jD91mZM2 on
Introduction
If you’ve been following my Redox Summer of Code progress, you might have noticed a long break after the last post. At first, the reason was that I just lost track of time. My previous years of RSoC have followed a similar inconsistent schedule, which I now refer to as an interval of one blog post per “programmer week”, where a “programmer week” is anywhere from 3 days to a month…
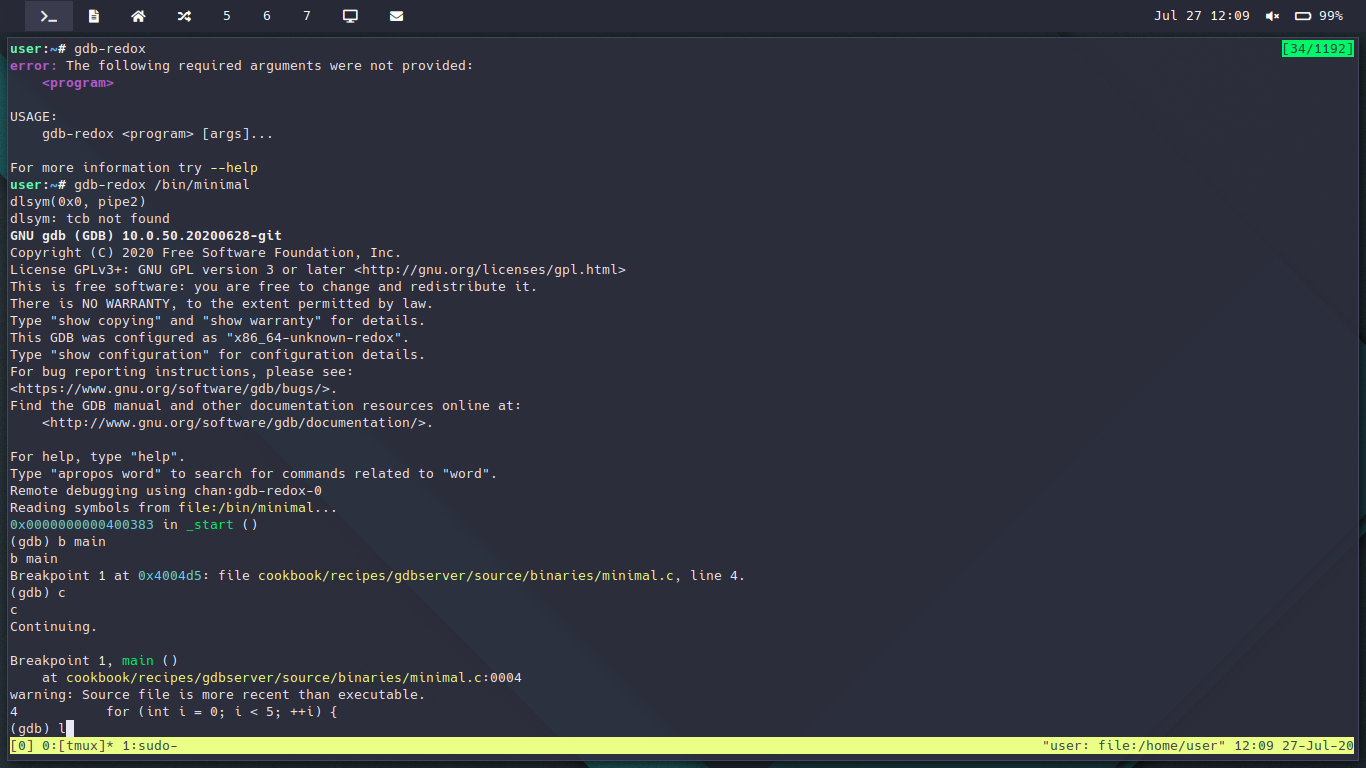
Now, the reason for not finishing is that I’m basically done! That’s right, GDB
has served us reliably for the past few weeks, where we’ve been able to debug
our dynamic linker (ld.so) and find problems with shared libraries. We got to
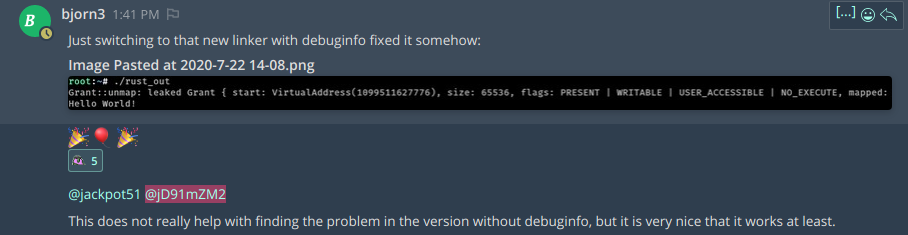
the point where the amazing @bjorn3 has managed to
run his first rust program compiled on Redox using his rustc cranelift
backend!
While obviously we would’ve found the bugs without gdb eventually, I’d love to attribute enough credit to it that it warrants being posted here!
Usage
The easiest way to use gdb on Redox, is to uncomment gdbserver and
gnu-binutils from your filesystem.toml, and run gdb-redox <absolute filepath> [args...]. It will launch our custom gdbserver and connect to it
from gdb over IPC. The
“disadvantage” of this is that you’re forced to copy your source code over to
Redox if you want pretty symbols and file numbers.
You can also choose to start the standalone gdbserver <absolute filepath> [args...], which will open a socket you can connect to from GDB. This allows
you to connect from a host Linux system using your favorite tools like normal,
by first running (gdb) target remote :64126 to connect to the running server.
This approach forces you to forward :64126 over the network, which can be done
by starting Redox with the net=redir flag.
Troubleshooting
If you’re having trouble getting Redox working, join me in our developer chat by sending an email to info@redox-os.org and asking for an invite link.